Introduction
Vomiting blood or passing black tarry stools? These are classic signs of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. This condition can be life-threatening. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and emergency response can make all the difference.
What is Upper GI Bleeding?
- Defined as bleeding from any source proximal to the ligament of Treitz (oesophagus, stomach, or duodenum)
- Common presentations: haematemesis (vomiting blood), melaena (black tarry stools), iron-deficiency anaemia
Key Clinical Presentations
Haematemesis
- Bright red or coffee-ground vomitus
- Indicates bleeding above the duodenojejunal junction
Melaena
- Black, tarry stool
- Indicates altered blood from upper GI tract
Haematochezia
- Usually lower GI bleeding
- Can result from massive upper GI bleed in rare cases
Major Causes of Upper GI Bleeding
Oesophagus
- Oesophageal varices – dilated veins from portal hypertension; large volume bleeding, life-threatening
- Mallory-Weiss tear – mucosal tear from vomiting; bright red blood after retching
- Oesophageal carcinoma – chronic, low-grade blood loss
- Acute reflux oesophagitis – small, red, associated with regurgitation
Stomach
- Gastric ulcer – classic cause, painless, often preceded by indigestion
- Gastric carcinoma – bleeding with weight loss, anorexia
- Erosive gastritis – NSAID or alcohol use; bright red small volume bleed
- Dieulafoy’s lesion – rare, sudden large volume bleed
Duodenum
- Duodenal ulcer – common cause; often causes melaena
- Aortoduodenal fistula – rare, post-AAA repair, massive haemorrhage
Important Clinical Features by Region (H2)
| Region | Common Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Oesophagus | Varices, carcinoma, tear | Vomiting blood, dysphagia |
| Stomach | Ulcers, gastritis, cancer | Haematemesis, indigestion |
| Duodenum | Ulcer, aortoenteric fistula | Melaena, back pain, PR bleeding |
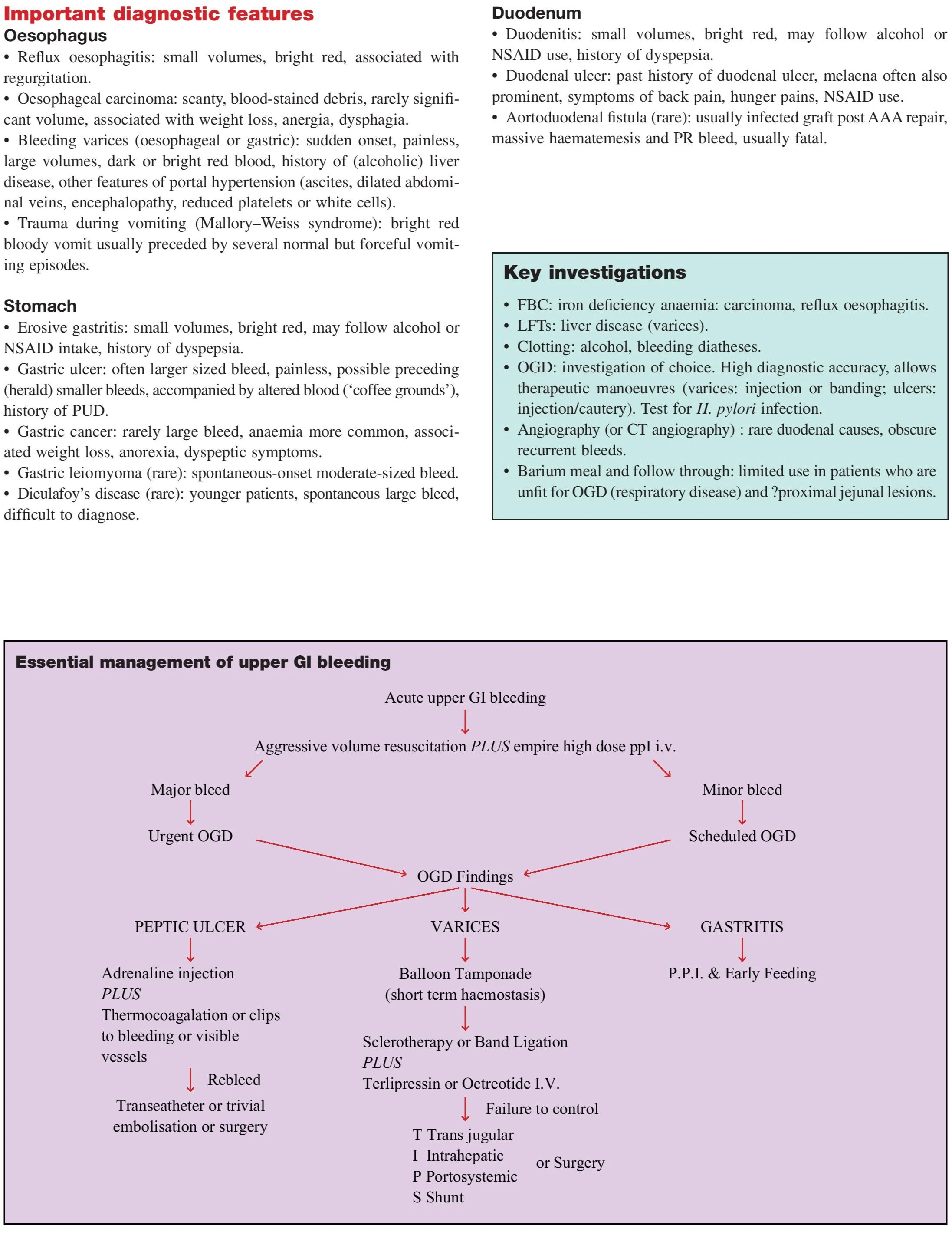
Diagnostic Workup
Laboratory Tests
- FBC – check hemoglobin, anemia
- LFTs – liver function for varices
- Coagulation profile – important before endoscopy
- Crossmatch – for transfusion
Endoscopy (OGD)
- Investigation of choice
- Diagnostic and therapeutic (adrenaline, clips, banding)
Imaging
- CT angiography – if bleeding is severe and OGD not revealing
- Barium meal – rarely used, only if OGD contraindicated
Management of Upper GI Bleeding
Initial Resuscitation
- ABC protocol
- IV access x2
- Crystalloids and blood products
- Monitor vitals and urine output
Medical Management
- IV PPI (proton pump inhibitor)
- Octreotide or terlipressin for varices
Endoscopic Therapy
Peptic Ulcer Bleed:
- Adrenaline injection + thermal coagulation
- Clips for visible vessel
Variceal Bleed:
- Band ligation or sclerotherapy
- Balloon tamponade (temporary)
- IV terlipressin or octreotide
Surgical or Radiological Intervention
- Indicated if endoscopic treatment fails
- Embolization
- TIPSS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt)
- Surgery (rarely needed)
Special Cases
1. Dieulafoy’s Lesion
- Sudden massive bleeding, hard to diagnose
- Requires endoscopic intervention
2. Mallory-Weiss Tear
- Associated with vomiting
- Self-limited in most cases
3. Aortoenteric Fistula
- Post-operative
- High fatality without emergency surgery
Prognosis and Follow-up
- Depends on cause and speed of intervention
- Varices have highest mortality
- Repeat endoscopy if rebleed suspected
- Follow-up with H. pylori testing for ulcer-related bleeds.
FAQs About Upper GI Bleeding
What is the most common cause of upper GI bleeding?
Peptic ulcer disease (gastric and duodenal).
Is vomiting blood always serious?
Yes. Haematemesis should always be evaluated immediately.
Can I have upper GI bleeding without visible blood?
Yes. Chronic bleeding can present with anaemia and fatigue.
How fast should upper GI bleed be treated?
Major bleeds are medical emergencies requiring urgent endoscopy.
Can endoscopy treat bleeding?
Yes. It’s both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Conclusion
Upper GI bleeding is a critical condition that needs swift diagnosis and management. Whether caused by ulcers, varices, or rare lesions, understanding the source and applying the right treatment can be lifesaving.
- Neck Lump: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Dysphagia: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Haemoptysis: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Breast Lump: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Breast Pain: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Nipple Discharge: Causes & Diagnosis
- Upper GI Bleeding: Causes & Diagnosis
- Lower GI Bleeding: Causes & Diagnosis
- Dyspepsia: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Acute Abdominal Pain: Causes & Diagnosis
- Chronic Abdominal Pain: Causes & Diagnosis
- Abdominal Swelling: Causes & Diagnosis
- Upper Abdominal Swelling: Causes
- Epigastric & Umbilical Abdominal Swelling
- Lower Abdominal Swelling: Causes
- Jaundice: Causes, Types & Diagnosis (LFT)
- Diarrhoea: Causes, Types & Diagnosis
- Altered Bowel Habit & Constipation
- Groin Swelling: Causes & Diagnosis
- Claudication: Leg Pain on Walking
- Acute Warm Painful Leg: Possible Causes
- Acute Cold Leg: Causes & Emergency
- Leg Ulceration: Types & Treatment
- Dysuria: Painful Urination
- Urinary Retention: Causes & Management
- Haematuria: Blood in Urine
- Scrotal Swellings: Differential Diagnosis
- Stomas & Surgical Incisions Care
- General Anaesthesia: Principles & Risks
- Regional Anaesthesia Types & Uses
- Hypoxia: Causes, Signs & Treatment
- Surgical Infections: Prevention & Management
- Post-Op Surgical Infections: Specific Types
- Sepsis: Recognition & Urgent Treatment
- Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
- Shock: Types & Clinical Management
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): Causes & Treatment
- Fractures: Types & Healing
- Congenital Childhood Orthopaedic Disorders
- Metabolic & Infective Bone Disorders
- Arthritis: Types & Management
- Musculoskeletal Tumours Overview
- Burns: Assessment & Treatment
- Major Trauma: Initial Management
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Nursing & Care
- GERD: Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease
- Oesophageal Carcinoma: Signs & Treatment
- Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
- Gastric Carcinoma: Diagnosis & Care
- Malabsorption: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
- Crohn’s Disease: Symptoms & Treatment
- Acute Appendicitis: Symptoms & Treatment
- Diverticular Disease: Symptoms & Treatment
- Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms & Treatment
- Colorectal Carcinoma: Symptoms & Treatment
- Benign Anal & Perianal Disorders
- Intestinal Obstruction: Causes & Symptoms
- Abdominal Hernias: Types, Symptoms & Surgery
- Gallstone Disease: Causes & Symptoms
- Gallstone Disease: Diagnosis & Surgery
- Pancreatitis: Causes & Management
- Pancreatic Tumours: Types & Treatment
- Benign Breast Disease
- Breast Cancer: Diagnosis & Treatment
- Goitre: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Thyroid Malignancies: Types & Symptoms
- Parathyroid Disease: Symptoms & Causes