The s-block elements are the first two groups of the periodic table, also known as Group 1 (Alkali Metals) and Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals). Here's a quick summary of their key features:
s-Block Elements - General Characteristics
Electron Configuration:
➭ Alkali metals (Group 1): 1 electron in the outermost s-orbital (ns¹).➭ Alkaline earth metals (Group 2): 2 electrons in the outermost s-orbital (ns²).
Chemical Properties:
➭ Form ionic compounds: React readily with non-metals to form ionic salts.Alkali Metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
➭ Highly reactive: React vigorously with water, forming strong bases (hydroxides).
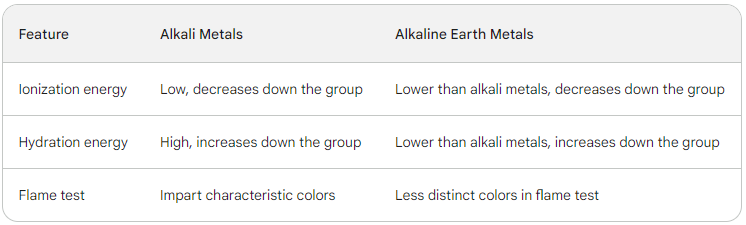
➭ Low ionization energies: Easily lose their single valence electron.
➭ Soft and light: Can be cut with a knife.
➭ Impart characteristic colors to flames: Li (crimson), Na (yellow), K (violet), Rb (red), Cs (blue).
Alkaline Earth Metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
➭ Less reactive than alkali metals: React with water slowly, forming less soluble hydroxides.
➭ Higher ionization energies: Need more energy to remove two valence electrons.
➭ Harder and denser than alkali metals: Except for Be, which is brittle.
Form stable oxides and carbonates.
s-Block Elements - Key Differences
s-Block Elements - Important Compounds
s-Block Elements - Specific Examples
Chemistry Short Notes 📚⌛
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Short Notes 📚
2. Atomic Structure — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
3. Periodic table — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
4. Chemical Bonding — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
5. States of matter — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
6. Thermodynamics — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
7. Chemical Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
8. Ionic Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
9. Redox Reaction — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
10. Hydrogen — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
11. P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Notes 📚