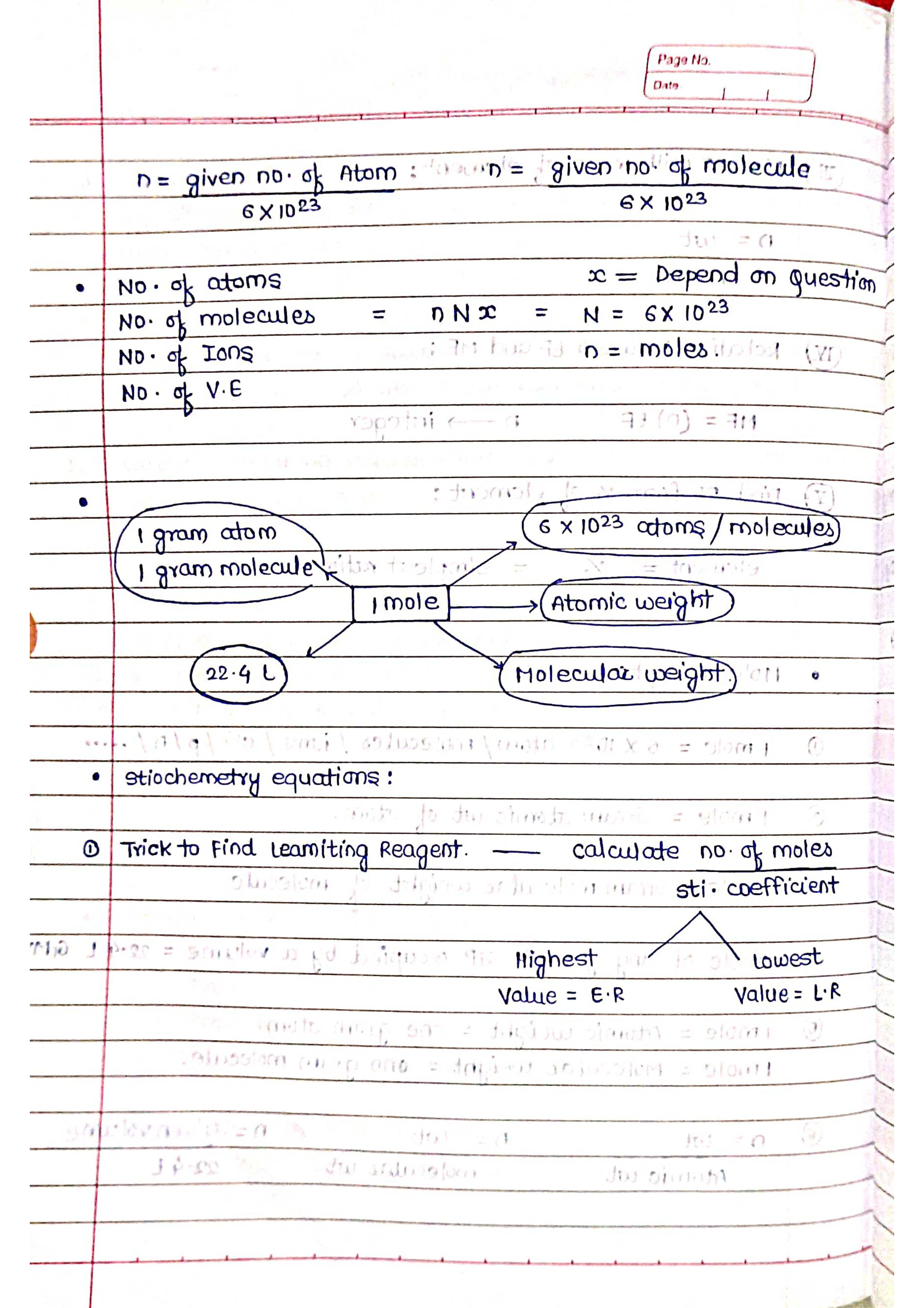
Chemistry is the fascinating study of matter, its properties, and the changes it undergoes. It's the science that underpins everything from the food we eat to the medicines we take to the materials that make up our world. Here's a brief overview of some fundamental concepts in chemistry:
1. Matter and its States
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It exists in three main states:
➡️Solid: Definite shape and volume (e.g., ice)2. Elements and Compounds
➭Elements are pure substances made up of only one type of atom (e.g., gold, oxygen). There are 118 known elements in the periodic table.3. Atoms and Molecules
➭Atoms are the tiny building blocks of matter. They are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons.4. Physical and Chemical Changes
➭Physical changes involve a change in the physical state or appearance of matter but not its chemical composition (e.g., ice melting into water).5. Chemical Reactions
1. Chemical reactions are processes in which reactants are transformed into products. They are represented by chemical equations.6. Measurement in Chemistry
➡️Scientific measurements are essential in chemistry. The International System of Units (SI) is used, with basic units like meter (m) for length, kilogram (kg) for mass, and second (s) for time.7. Important Laws in Chemistry
➭Law of conservation of mass: In a closed system, the total mass of matter remains constant before, during, and after a chemical reaction.Chemistry Short Notes 📚⌛
1. P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Notes 📚
2. Atomic Structure — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
3. Periodic table — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
4. Chemical Bonding — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
5. States of matter — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
6. Thermodynamics — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
7. Chemical Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
8. Ionic Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
9. Redox Reaction — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
10. Hydrogen — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
11. S-Block Elements - Chemistry Short Notes 📚


![Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF] 📚 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF] 📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgdKcQyXO_QyF7P8YynBkTMKRnOuAf9Ri5bhVlKpt30BSoJ_JVjGUQpyKsHbXGoqU7qQX2FTBExN1yRXg3KVkQEQj-ufXEoCF5fzHWBgr_dXEHP418M7as2Q_CflEJEWI_sfQAUi3KVqUNt0TW8L6KCZYUdnQrzrPAZV9WtKulaXg1L0cA_Y6-XFBXrULo/s16000-rw/Some%20Basic%20Concept%20of%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes%20(2).jpeg)

![Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF] 📚 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF] 📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgxrfDflVnVpxc57G1J8vZOwEAoEz2RHLYNSV9NSw-a1EkPmWhM8-E5bc9IvJ4PADdVawYs82Qh08Z3tfqYYTmOe_MKiZoJP0F5eznVwdRQZicdeHUhG4uKPlpCyUcoHUhUzzbueqFx-A0eJ_be2wVTcDQdUofJesel4YELSy3HMsVhDy3oQ6l9_fg-daM/s16000-rw/Some%20Basic%20Concept%20of%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes.jpeg)