1. Introduction:
➡️ Solid state is one of the three fundamental states of matter (solid, liquid, gas).
➡️ Solids have definite shape and volume, strong intermolecular forces, and minimal empty space.
➡️ Solid-state chemistry deals with the structure, properties, and applications of solids.
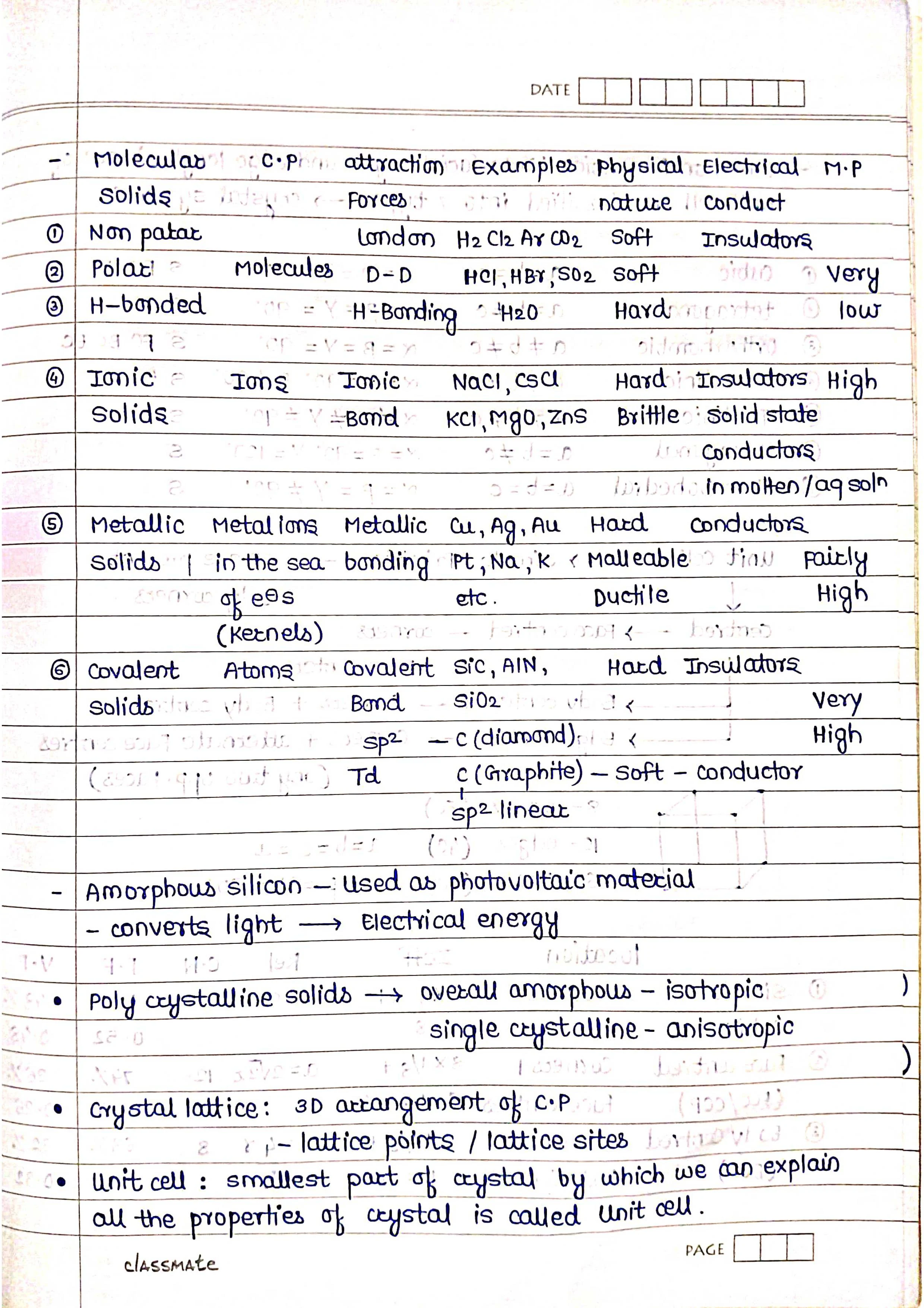
2. Classification of Solids:
Based on Bonding:
➭ Ionic solids: Held by electrostatic forces between ions (e.g., NaCl).
➭ Covalent solids: Held by shared electrons between atoms (e.g., diamond).
➭ Metallic solids: Held by delocalized electrons in a metallic sea (e.g., copper).
➭ Molecular solids: Held by weak intermolecular forces between molecules (e.g., ice).
Based on Crystal Structure:
➭ Crystalline solids: Have a well-ordered, repeating arrangement of atoms/molecules (e.g., salt).
➭ Amorphous solids: Lack a regular arrangement (e.g., glass).
3. Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells:
➭ Crystal lattice: A 3D network of points representing the positions of atoms/molecules.
➭ Unit cell: The smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice.
➭ Bravais lattices: 14 fundamental types of unit cells based on symmetry.
➭ Packing efficiency: The fraction of space occupied by spheres representing atoms/molecules in a unit cell.
4. Important Concepts:
➭ Coordination number: Number of nearest neighbors an atom/molecule has in a crystal.
➭ Radius ratio rule: Predicts the type of crystal structure based on the size ratio of cations and anions.
➭ Voids: Empty spaces between atoms/molecules in a crystal lattice.
➭ Crystal defects: Irregularities in the crystal structure (e.g., vacancies, interstitials).
5. Properties of Solids:
➭ Melting point: Temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid.
➭ Hardness: Resistance to scratching or deformation.
➭ Electrical conductivity: Ability to conduct electricity.
➭ Thermal conductivity: Ability to conduct heat.
➭ Band theory: Explains the electrical properties of solids based on the energy levels of electrons.
Chemistry Handwritten Short Notes 📚 for Class 11 & 12 | Free PDF Downloads
6. Applications of Solid State Chemistry:
➭ Semiconductors: Used in electronic devices like transistors and integrated circuits.
➭ Superconductors: Conduct electricity with zero resistance at low temperatures.
➭ Ceramics: Used in construction, electronics, and other applications.
➭ Polymers: Large molecules with diverse properties used in various materials.
Note: These are just short notes, and many more details and concepts exist within solid-state chemistry.