Hydrogen, the first element on the periodic table, is unique and fascinating due to its unusual properties. Here are some key points to remember:
Hydrogen - Basics
➭ Symbol: H
➭ Atomic number: 1
➭ Position: Top left of the periodic table (not quite fitting in with a group)
➭ Isotopes: Protium (H-1, most abundant), Deuterium (D or H-2), Tritium (T or H-3, radioactive)
➭ Most abundant element in the universe (mostly as diatomic hydrogen, H₂)
Hydrogen - Physical properties
➭ Colourless, odourless, tasteless gas
➭ Lowest density of all elements
➭ Highly flammable
➭ Poorly soluble in water
Hydrogen - Chemical properties
➭ Highly reactive
➭ Can form covalent bonds with most elements
➭ Can act as a reducing agent (gains electrons)
➭ Forms ionic compounds with metals and some non-metals
Hydrogen - Important compounds
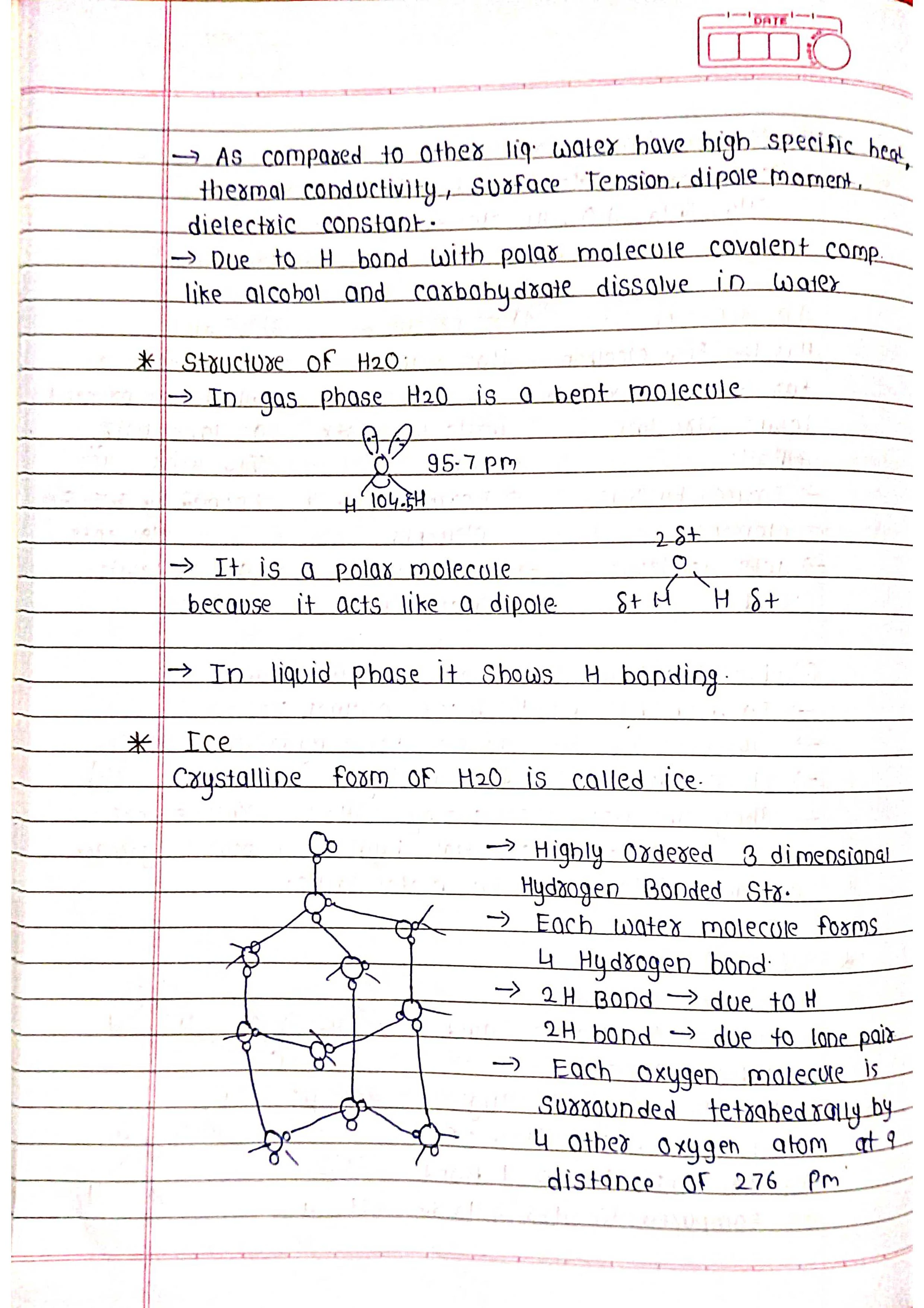
➭ Water (H₂O): Essential for life, a polar molecule with unique properties due to hydrogen bonding.
➭ Hydrocarbons: Organic compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon, the basis of most fuels and many other materials.
➭ Hydrogen halides (HX): Acids formed by the reaction of hydrogen with halogens (e.g., HCl, HF).
➭ Ammonia (NH₃): Important industrial chemical and agricultural fertilizer.
Chemistry Handwritten Short Notes 📚 for Class 11 & 12 | Free PDF Downloads
Hydrogen - Applications
➭ Fuel: Can be burned cleanly to produce energy, potential future fuel source.
➭ Fuel cells: Efficiently converts hydrogen and oxygen into electricity.
➭ Hydrogenation: Used in food processing and other industrial applications.
➭ Rocket fuel: Used in some high-performance rockets.
Hydrogen - Important reactions
➭ Combustion with oxygen: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O (releases significant energy)
➭ Reaction with halogens: H₂ + X₂ → 2HX (X = F, Cl, Br, I)
➭ Haber-Bosch process: N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH₃ (production of ammonia)
Hydrogen - Additional notes
➭ Hydrogen is unique due to its small size and single electron.
➭ It has a complex position in the periodic table, exhibiting properties of both metals and non-metals.
➭ Hydrogen research is ongoing, with potential applications in various fields like energy storage and clean transportation.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Chemistry Short Notes 📚⌛
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Short Notes 📚
2. Atomic Structure — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
3. Periodic table — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
4. Chemical Bonding — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
5. States of matter — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
6. Thermodynamics — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
7. Chemical Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
8. Ionic Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
9. Redox Reaction — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
10. P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Notes 📚
11. S-Block Elements - Chemistry Short Notes 📚


![Hydrogen - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚 Hydrogen - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEic6QCmZXdHZORcpOcpTL5EfeKuD44btNTAOyq4wJZ5FDoEswcgfwj6OYKxSqYxZ10HuzQJBaFLRPH6V-eAyov175cjweDnCbNJPFBaGMJlKUxBPIMowJhw3pAiAjOjQ10gbCgVuerYqQ-eP6p9iqt3317NU36BOmpGDNDrrQxLASnOdFWLEyAVhV0mivk/s16000-rw/Hydrogen%20-%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes%20%5BPDF%5D%F0%9F%93%9A.jpeg)

![Hydrogen - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚 Hydrogen - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjGjfRTBxOzfhtaXNRpYK3ZSjDVprB_qltfIjE09ki5-gZB1uyqjYf3o4QgoIPL-sK4DQJsmkIeTBamXlANiAtp1Ljmf37OyhGkMlwaqLvXAqYFGEwbblxLoXG2arbmby3H-mU2Ia_1DR5KWbNsB1jqh8_cKn8rQtCVlhQiyQZKau1bos6lLKQFXyB7OX0/s16000-rw/Hydrogen%20-%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes%20%5BPDF%5D%F0%9F%93%9A%20(2).jpeg)
