Protected Area Network in India - India, known for its rich biodiversity, is one of the 17 mega-diverse countries in the world. With only 2.4% of the world's land area, it supports approximately 8% of the known global biodiversity. Recognizing the importance of preserving its natural heritage, India has established a robust network of protected areas that serve as sanctuaries for endangered species and unique ecosystems.
What is a Protected Area Network?
A Protected Area Network refers to designated regions where biodiversity, ecosystems, and cultural resources are protected under legal frameworks. These areas aim to conserve wildlife, preserve natural habitats, and sustain ecological balance. India's Protected Area Network includes national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, conservation reserves, and community reserves.
Overview of Protected Areas in India
India has a total of 668 protected areas, covering 161,221.57 sq. km, which is about 4.9% of the country's total geographic area. These include:
- 102 National Parks
- 515 Wildlife Sanctuaries
- 47 Conservation Reserves
- 4 Community Reserves
Types of Protected Areas
1. National Parks
National Parks are areas with significant ecological, faunal, and floral importance. They are established to protect wildlife and their natural habitat. In these areas:
- No human activities, including grazing or extraction of resources, are permitted.
- Strict legal protection ensures the preservation of biodiversity.
2. Wildlife Sanctuaries
Wildlife Sanctuaries are similar to National Parks but with some differences:
- Limited human activities, such as grazing, may be allowed.
- People living within sanctuary boundaries can retain certain rights.
3. Conservation Reserves
Conservation Reserves are areas owned by the government and established adjacent to national parks or sanctuaries. They aim to link protected areas and conserve landscapes and ecosystems while involving local communities in conservation efforts.
4. Community Reserves
Community Reserves are created in private or community-owned lands where local people volunteer to conserve biodiversity. They protect not only flora and fauna but also traditional conservation practices.
Notable Protected Areas in India
World Heritage Sites
India has five protected areas designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites for their exceptional biodiversity:
- Kaziranga National Park, Assam
- Keoladeo National Park, Rajasthan
- Manas National Park, Assam
- Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks, Uttarakhand
- Sundarbans National Park, West Bengal
Biodiversity Hotspots
India hosts four biodiversity hotspots:
- Himalayas
- Indo-Burma Region
- Western Ghats
- Sundaland (Nicobar Islands)
These regions are recognized for their rich endemic species and are prioritized for conservation.
Key Initiatives and Programs
1. Project Tiger
Launched in 1973, Project Tiger focuses on conserving India's tiger population and its habitats. Currently, there are 39 tiger reserves covering over 72,749 sq. km.
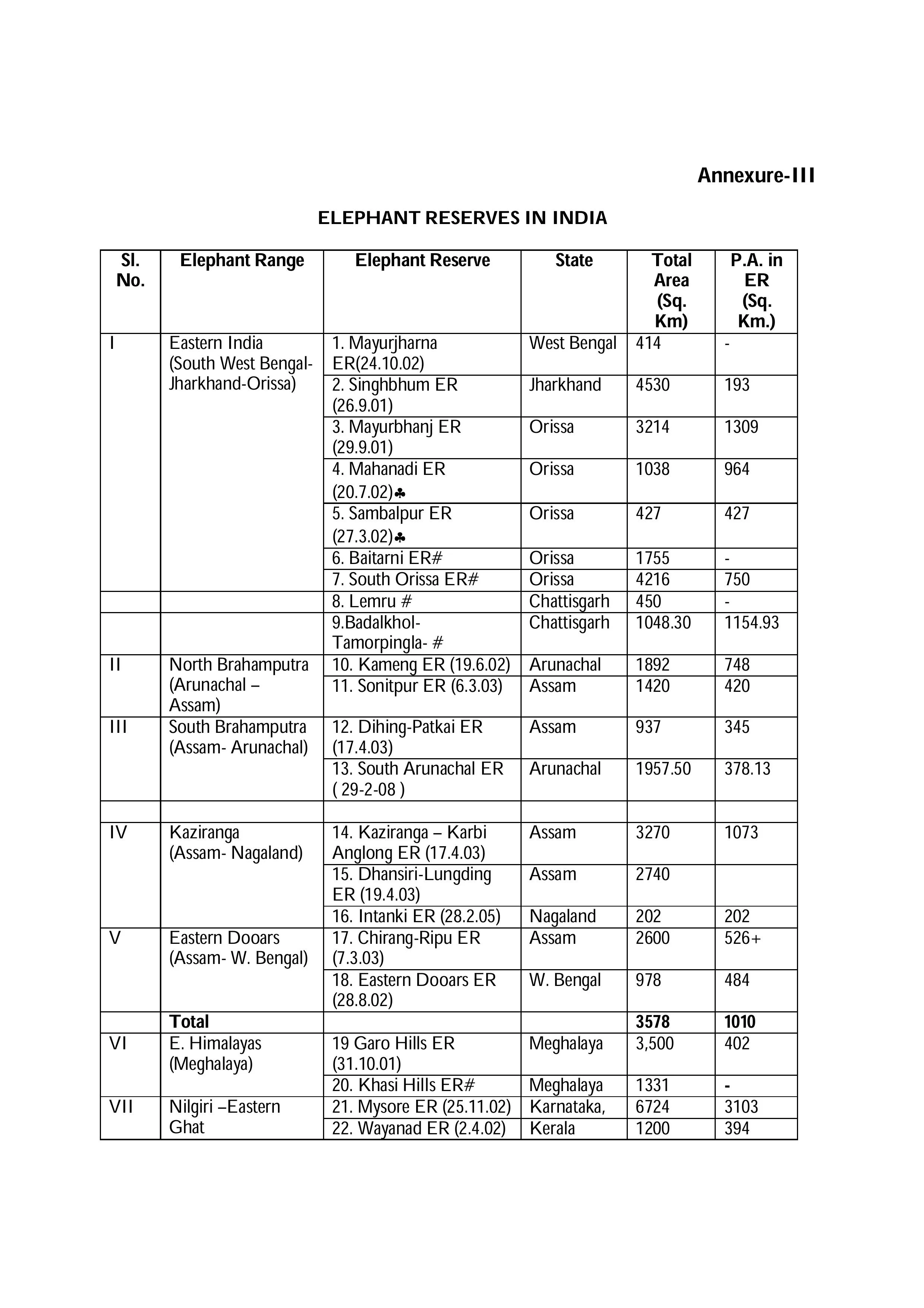
2. Project Elephant
Initiated in 1992, Project Elephant aims to protect elephants and their habitats. It includes the establishment of 30 elephant reserves across India.
3. Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats
This scheme provides financial support for managing wildlife habitats, protecting endangered species, and addressing human-wildlife conflicts.
Challenges in Protected Area Management
1. Habitat Fragmentation
Development projects such as roads, dams, and urbanization disrupt wildlife corridors and habitats.
2. Human-Wildlife Conflicts
Encroachments and loss of natural habitats lead to increased interactions between humans and wildlife, often resulting in conflicts.
3. Poaching and Illegal Trade
Illegal hunting and trade of wildlife threaten many species, including tigers, elephants, and pangolins.
4. Livelihood Dependence
Communities living near forests rely heavily on forest resources, creating additional pressures on ecosystems.
Legal Framework for Protected Areas
Protected Areas in India are governed under various laws, including:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Provides the framework for establishing and managing protected areas.
- Forest Conservation Act, 1980: Regulates deforestation and the use of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002: Ensures the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
- Environment Protection Act, 1986: Provides a mechanism to address environmental challenges.
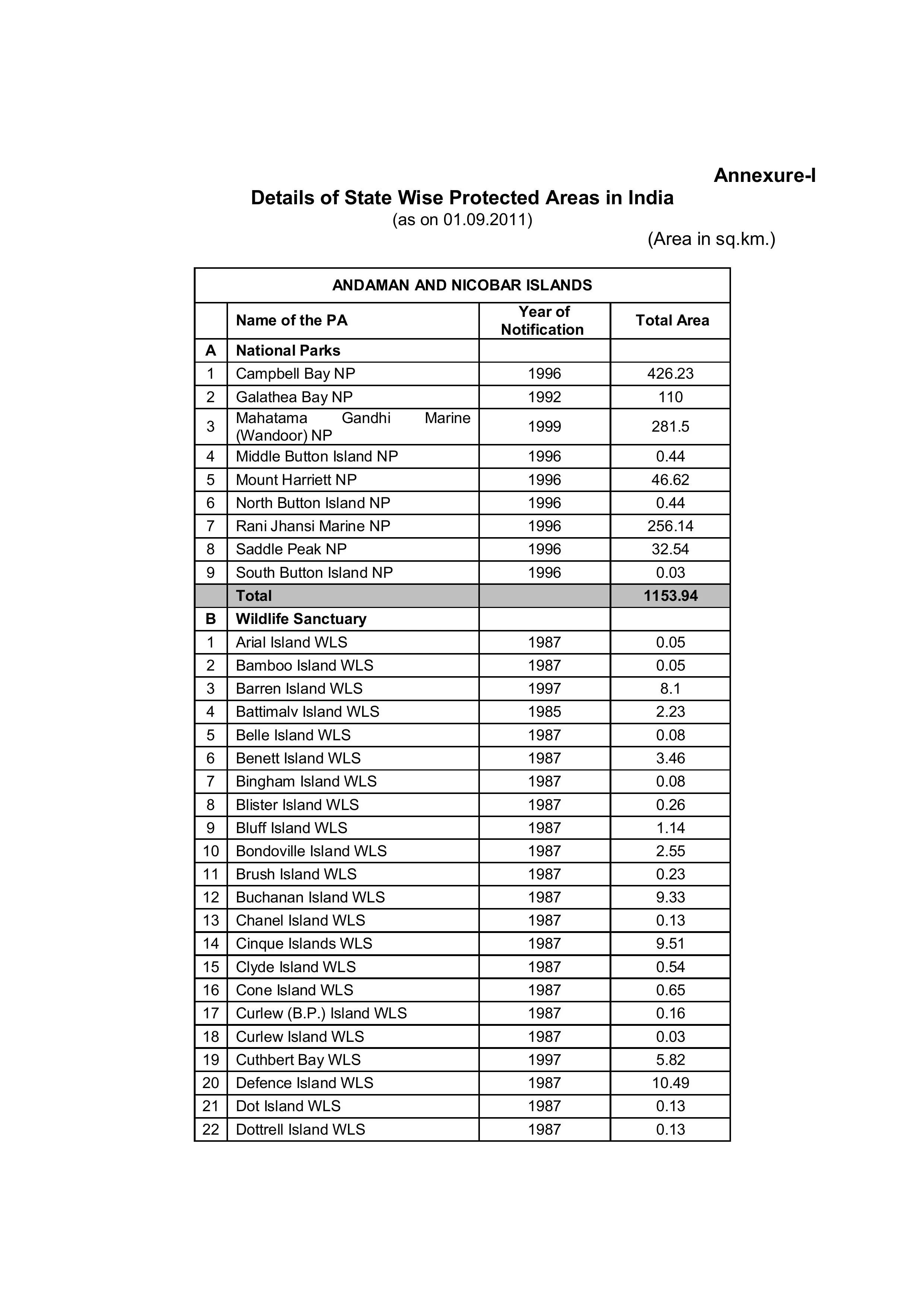
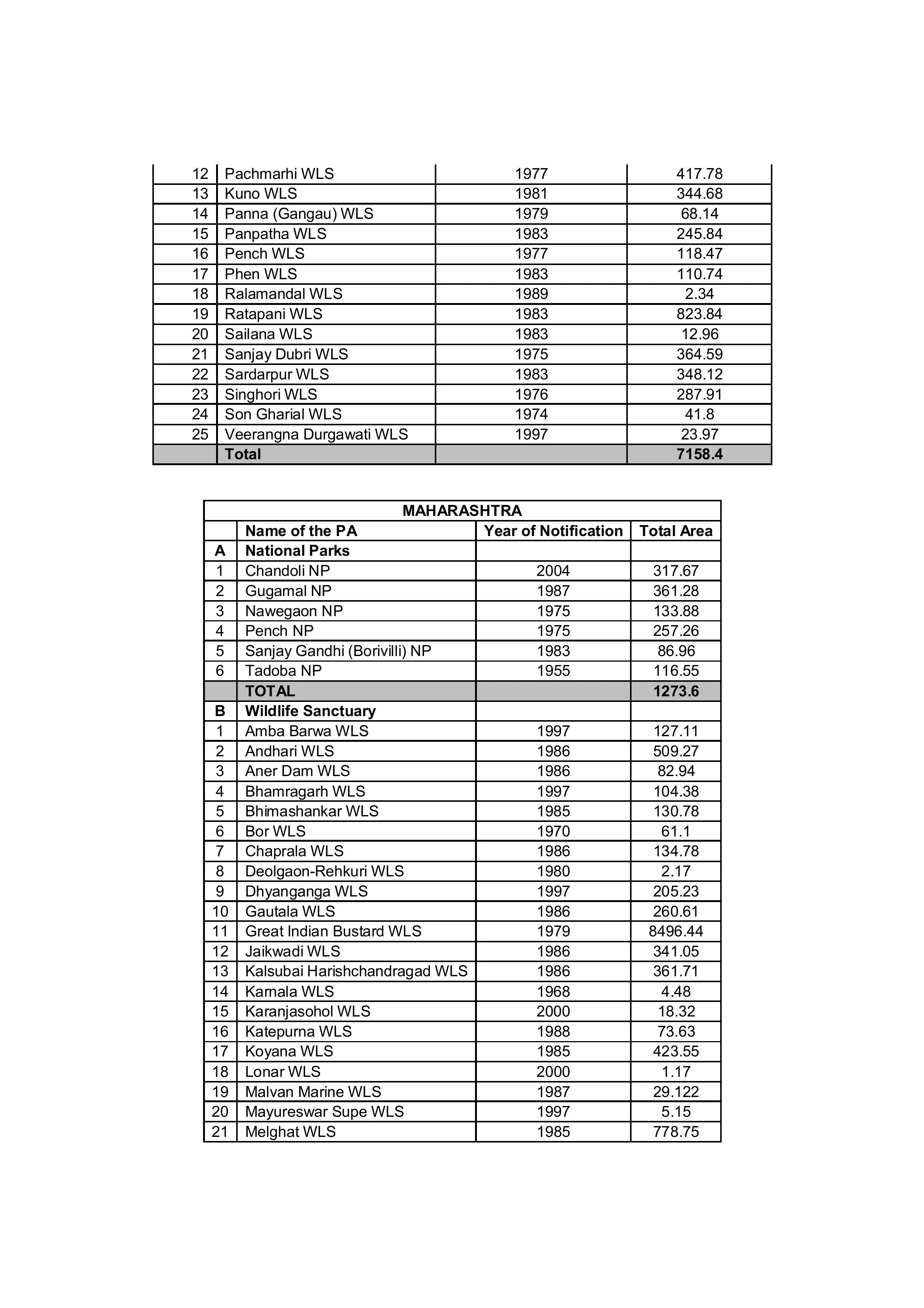
State-Wise Distribution of Protected Areas
India's protected areas are distributed across all states and union territories. For instance:
- Madhya Pradesh: 9 National Parks and 25 Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands: 9 National Parks and 96 Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- Assam: Home to Kaziranga and Manas National Parks, known for their rhino and tiger populations.
Trans-Boundary Protected Areas
India has initiated trans-boundary conservation efforts with neighboring countries. Examples include:
- Sundarbans: Shared with Bangladesh, it supports a thriving population of Royal Bengal Tigers.
- Manas: Linked with Bhutan for wildlife and habitat conservation.
Future of Protected Areas in India
To ensure the sustainability of its rich biodiversity, India must:
- Strengthen conservation policies and enforcement mechanisms.
- Promote community-based conservation efforts.
- Enhance global cooperation for species protection and habitat restoration.
FAQs About Protected Areas in India
What is the largest national park in India?
Hemis National Park in Ladakh, spanning 4,400 sq. km, is the largest national park in India.How many biosphere reserves does India have?
India has 18 biosphere reserves, including the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve and the Gulf of Mannar.What is the difference between a National Park and a Wildlife Sanctuary?
National Parks have stricter regulations, prohibiting human activities, while Wildlife Sanctuaries may allow limited human activities under certain conditions.Why are conservation reserves important?
Conservation reserves connect fragmented habitats, promoting ecological balance and the movement of wildlife.How does India involve local communities in conservation?
Community Reserves and initiatives like eco-tourism involve local people in wildlife conservation, ensuring their livelihoods are supported.India's Protected Area Network plays a crucial role in preserving its unparalleled biodiversity. Through continued efforts and public awareness, the country can safeguard its natural heritage for future generations.