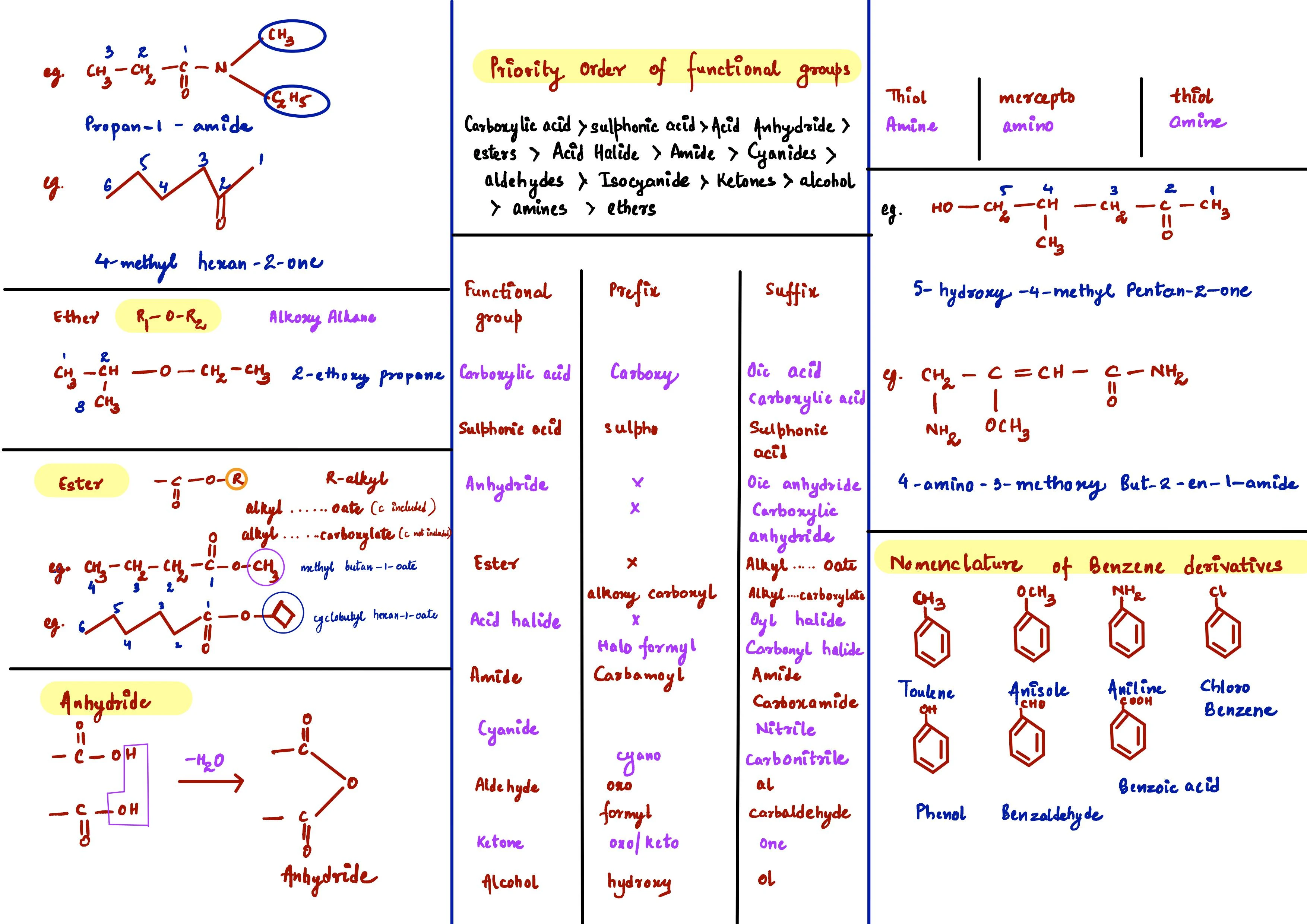
IUPAC Nomenclature - The provided text outlines the IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds, including various functional groups and substituents. It emphasizes selecting the longest continuous carbon chain, proper numbering to give substituents the lowest possible numbers, and the importance of branching in determining the main chain. The text also discusses the priority of functional groups and how to alphabetically order substituents.
Examples of different compounds and their nomenclature, such as alcohols, aldehydes, and amines, are included to illustrate the naming conventions. Overall, it serves as a guide for understanding the systematic naming of organic molecules.
Longest Chain Selection: Identify the longest continuous carbon chain; prioritize chains with more branches if lengths are equal.
Numbering: Assign numbers to ensure substituents receive the lowest possible numbers; resolve ties by alphabetical order.
Functional Groups: Recognize functional groups (e.g., alcohols, aldehydes, amines) and their priority in naming.
Prefixes and Suffixes: Use appropriate prefixes (di, tri, tetra) and suffixes based on functional groups.
Benzene Derivatives: Apply specific naming conventions for substituted benzene compounds.
IUPAC Nomenclature - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚
Key Insights
- The longest continuous carbon chain is prioritized for naming.
- Substituents must be numbered to minimize their numerical designation.
- When confronted with identical carbon counts, the chain with more branches is favored.
- Alphabetical order is crucial when multiple substituents are present, regardless of their numerical designation.
- Different functional groups (e.g., alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids) have defined priorities that influence the overall name of the compound.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of the longest carbon chain in IUPAC nomenclature?
The longest carbon chain is selected as it forms the backbone of the compound, determining its base name and functional group classification.
How is numbering done in IUPAC nomenclature?
Numbering is done to assign the lowest possible numbers to the substituents, ensuring clarity and accuracy in the compound’s name.
Why are functional groups prioritized in naming?
Functional groups dictate the chemical properties of the molecule, making their identification essential for proper nomenclature and understanding of the compound’s behavior.
How do you determine the order of substituents in a compound?
Substituents are ordered alphabetically when listing them in the compound’s name, irrespective of their position numbers, to ensure consistent naming conventions.