Preparing for the Class 12 Physics examination requires a strategic approach to effectively cover the vast syllabus. This guide provides a concise overview of each chapter, highlighting key concepts and essential points to aid in your revision.
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields
- Properties of electric charge (additivity, conservation).
- Coulomb’s Law and electric field concepts.
- Gauss’s Law and applications.
Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Electrostatic potential and potential energy.
- Capacitance and factors affecting it.
- Role of dielectrics in capacitors.
Chapter 3: Current Electricity
- Electric current, resistance, and resistivity.
- Kirchhoff’s Laws and their applications.
- Meter bridge and Wheatstone bridge.
Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism
- Magnetic field due to current-carrying wire.
- Ampere’s Circuital Law and solenoids.
- Moving coil galvanometer and its conversion into an ammeter and voltmeter.
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter
- Earth’s magnetism and its components.
- Magnetic properties of materials.
- Hysteresis and magnetic susceptibility.
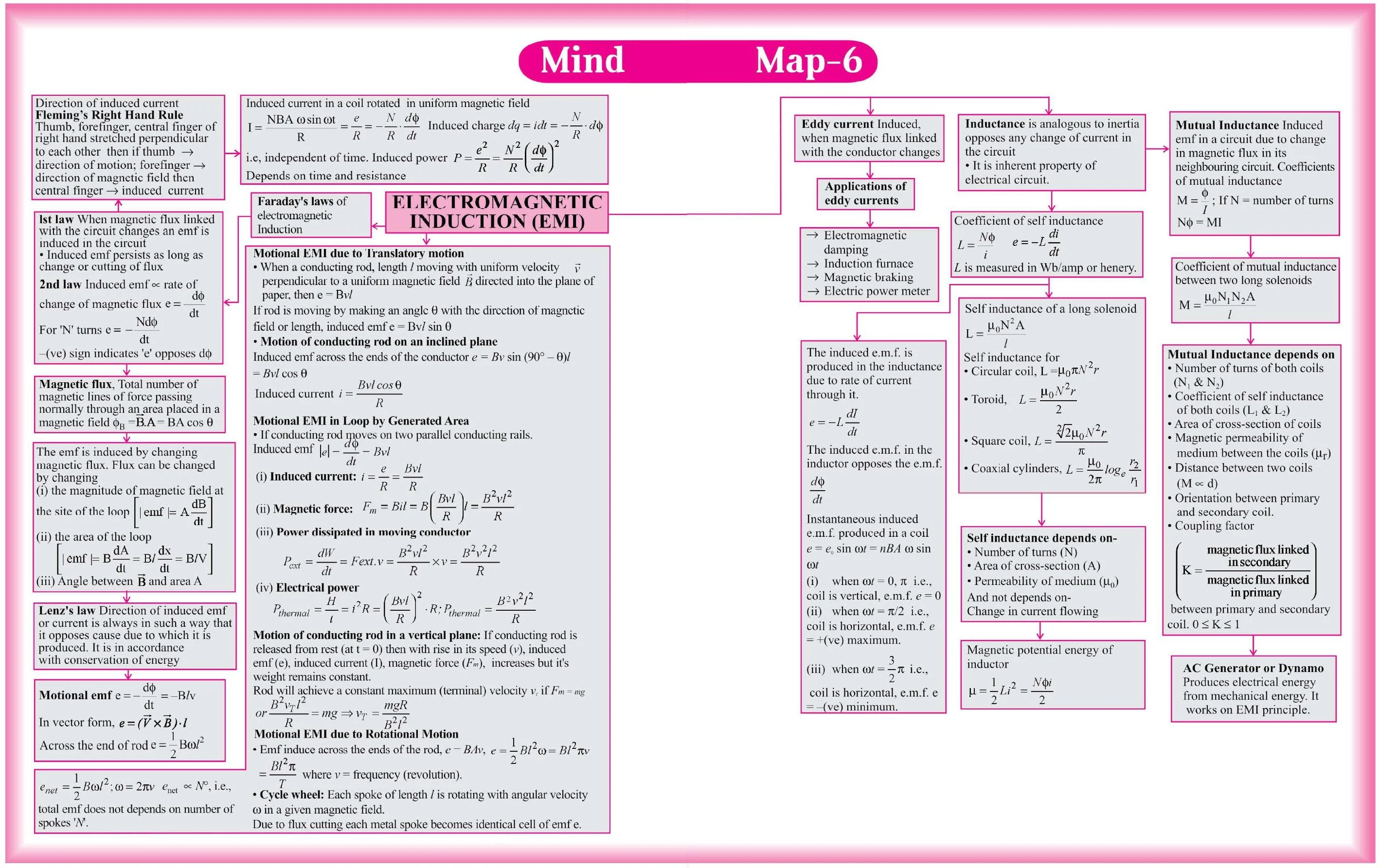
Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday’s and Lenz’s Laws.
- Eddy currents and their applications.
- Mutual and self-inductance.
Chapter 7: Alternating Current
- Alternating current (AC) and its characteristics.
- Reactance, impedance, and resonance.
- Working of transformers and power transmission.
Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
- Maxwell’s equations and wave propagation.
- Properties and applications of electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnetic spectrum and its significance.
Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Reflection, refraction, and lens formula.
- Total Internal Reflection and its applications (optical fibers).
- Working of microscopes and telescopes.
Chapter 10: Wave Optics
- Interference, Young’s double-slit experiment.
- Diffraction and its types.
- Polarization and its practical applications.
Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Photoelectric effect and Einstein’s explanation.
- Wave-particle duality.
- De Broglie hypothesis and matter waves
Chapter 12: Atoms
- Rutherford’s alpha particle scattering experiment.
- Bohr’s atomic model and energy levels.
- Spectral lines and hydrogen spectrum.
Chapter 13: Nuclei
- Nuclear composition and mass defect.
- Radioactive decay and its types.
- Nuclear fission and fusion.

Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics
- Energy bands in solids (conductors, insulators, semiconductors).
- Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
- p-n junction diode and its applications (LED, solar cells, rectifiers).
- Logic gates (AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR) and Boolean algebra.
Chapter 15: Communication Systems
- Elements of communication systems (transmitter, channel, receiver).
- Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM).
- Propagation of electromagnetic waves (ground wave, sky wave, space wave).
- Role of satellites in communication and fiber optics.